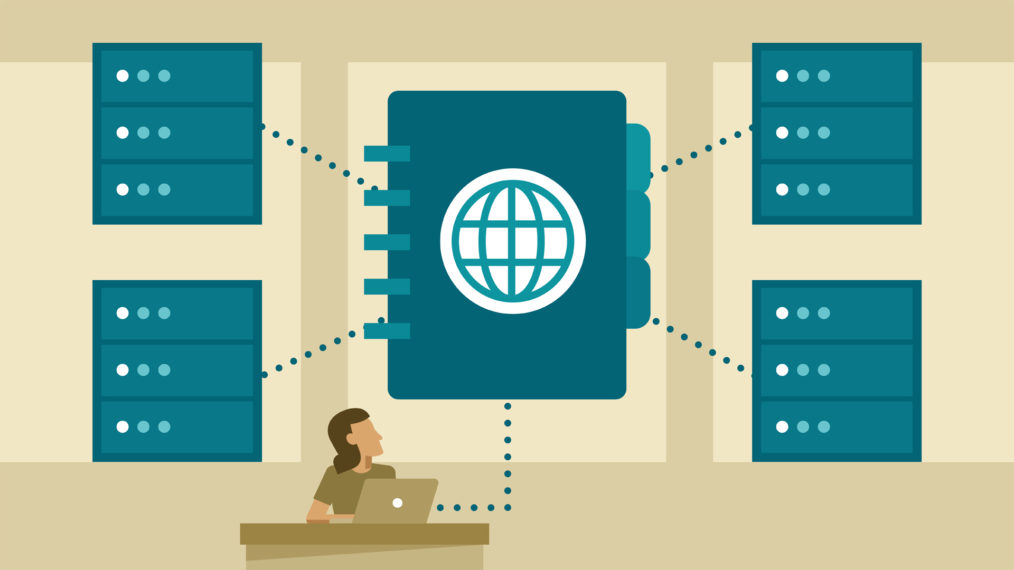
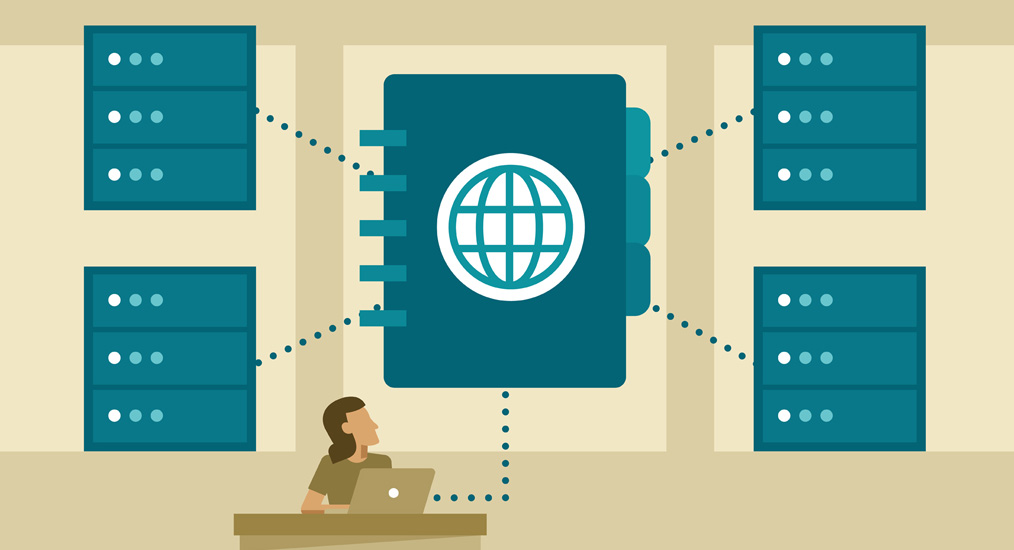
DNS forms the backbone of the internet. Without DNS, we would have to remember the individual IP addresses of the websites we need to access. DNS is the technology that allows us to navigate the web using names (www.example.com) we can remember and relates those names to the corresponding IP. In short, DNS makes the web navigable.
As times change, so do the developments in any industry. In this article we are going to discuss some latest DNS industry trends that you should know about.
GirlsWhoLie .Tube – TLD of Entertainment
 .tube TLD seem to be the thing in 2019. Used by industry leaders, it’s dedicated to websites that offer free video clips in variety of categories. With example of Girls Who Lie studio we can show you the very best that it’s to go offer – right under girlswholie.tube domain. This series, produced by Nubiles, is showing you how quickly lying girls are receiving their karma back. Trying to trick guys, they get tricked in the end – and paying high price for it.
.tube TLD seem to be the thing in 2019. Used by industry leaders, it’s dedicated to websites that offer free video clips in variety of categories. With example of Girls Who Lie studio we can show you the very best that it’s to go offer – right under girlswholie.tube domain. This series, produced by Nubiles, is showing you how quickly lying girls are receiving their karma back. Trying to trick guys, they get tricked in the end – and paying high price for it.
.Com Is Still The Leader
Notwithstanding the presence of several, more fancy (and some astonishing) Top Level Domains (TLD), .com is still the king. Even though new companies are using new TLDs such as .ai and country specific TLDs, .com is without a doubt the favorite among professionals. Being the most recognizable, easily remembered and user-friendly extension, it is expected that .com will continue to hold its top position in the DNS world now and in the future.
The Future Is Cloudy
 Currently, one of the major shifts in the DNS industry is in the form of a shift towards cloud-based platforms. As the rise of the cloud-computing ecosystem begins to pervade the internet, clients will have greater flexibility to control their DNS performance and improve user experience the world over. In the future, which includes now, most businesses will be shifting towards cloud-based DNS or use a hybrid DNS-Cloud setup by dividing their traffic between the regular DNS and Cloud infrastructure.
Currently, one of the major shifts in the DNS industry is in the form of a shift towards cloud-based platforms. As the rise of the cloud-computing ecosystem begins to pervade the internet, clients will have greater flexibility to control their DNS performance and improve user experience the world over. In the future, which includes now, most businesses will be shifting towards cloud-based DNS or use a hybrid DNS-Cloud setup by dividing their traffic between the regular DNS and Cloud infrastructure.

DNSSEC Adoption
DNSSEC is one of the current trends that anyone in the DNS Industry cannot afford to ignore. An abbreviation of Domain Name System Security Extensions, DNSSEC acts as the security mechanism of the DNS. The DNS system may be susceptible to multiple cyber security threats like man-in-the-middle or DDoS attacks. DNSSEC helps to protect DNS from such threats by applying digital signatures to DNS data, thereby validating the origin of and ensuring reliable movement of data over the internet.
DNS For CDN
As more and more internet services move to the cloud, international websites are turning to Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) in order to provide quality services to their audiences. This means that DNS services are forced to reinvent the way they manage their records, taking into account the fact that CDNs are dynamic and change IPs based on the users’ locations. One such example is how DNS Made Easy remodeled the DNS record for CDNs; known as ANAME records, these can perform the functionality of CNAME at the root level, thus changing the way how DNS zones can be configured.
Custom TLDs
 In spite of the dominance of .com, new variations on TLDs are also gaining popularity. Region-specific domains such as .us, .io or .in are already gaining prominence. Along with entertainment related domains like .movie or .music, profession specific domains such as .consultant and .realtor are also carving out their own niches and cannot be ignored.
In spite of the dominance of .com, new variations on TLDs are also gaining popularity. Region-specific domains such as .us, .io or .in are already gaining prominence. Along with entertainment related domains like .movie or .music, profession specific domains such as .consultant and .realtor are also carving out their own niches and cannot be ignored.
Greater Granularity
DNS traffic management is now able to offer greater level of granularity in its operation. As most growing companies discover, clients and customers represent a wide demographic which requires innovative and targeted ways to reach them. Your customers may be segmented based on language, geographic or interest-based parameters. Thanks to advantages in cloud and geo-location technologies, DNS can now help you to reach audiences based on unique identifiers such as IP, geo-location and many more such segments. Whether you are a large business looking to launch a vast marketing campaign or a startup targeting a niche market, DNS granular targeting can help augment your efforts.
Keeping It Short
Short domain names are another trend that anyone in the DNS Industry should be aware of. Instead of long keyword-based domain names intended to manipulate search rankings, the trend is increasingly moving towards short and memorable names which users can easily remember, and hence use frequently. Case in point: tinydns.org. Need we say more?
Conclusion
The only constant thing about trends is that they change. The above lists some of the latest in the DNS industry. The DNS ecosystem is complex, and we hope the above points will help you navigate it well.



















 Unbound
Unbound PowerDNS
PowerDNS Erl-DNS
Erl-DNS Dnsmasq
Dnsmasq Microsoft DNS
Microsoft DNS